Google AI Overviews are changing how search results look, not how rankings work. This guide covers where they appear, what content gets cited, and how to measure their impact on your traffic. No new acronyms to learn. No tools to buy. Just practical SEO analysis you can apply this week.
The Reality of AI Overviews in Search
Google AI Overviews now often appear above organic results for a growing percentage of queries. They synthesize answers from multiple sources into a single block, and they’re changing how users interact with search results.
The SEO industry response has been predictable. New acronyms (GEO, AEO, LLMO), new tools, new courses, new panic. Some people are telling you to restructure your entire content strategy. Others are dismissing AI Overviews entirely because “Google said traditional SEO still works.”
Both responses miss the point.
Google has confirmed that normal SEO practices work for AI Overview inclusion. That’s true. But “just do SEO” without understanding how AI Overviews are changing visibility and click behavior is lazy advice. You need to know where they appear, what content they pull from, and how to measure their impact on your traffic.
This guide covers the practical work. No tool dependencies. No hype. No pretending you need to become a prompt engineer to rank in search.
What Google Has Actually Said About AI Overviews
Google’s official position comes down to a few key points:
AI Overviews are generated from existing indexed content. They pull from pages that already rank well in traditional search. You don’t need separate “LLM optimization” or special files to be included.
Danny Sullivan and John Mueller have been explicit about this. In a recent Search Off the Record episode, they warned against restructuring content into tiny chunks just to appeal to AI systems. Their message: write for humans, and the AI will handle it.
Google’s product expert Kenichi Suzuki has also confirmed that normal SEO practices work for AI Overview rankings. No special sauce required.
Here’s how to translate that into reality:
What “Do Good SEO” Actually Means
- Your pages need to be crawlable and indexed
- Your content needs to match search intent
- You need topical authority and trust signals
- Technical fundamentals still matter
What “Do Good SEO” Doesn’t Mean
- Ignore AI Overviews completely
- Stop analyzing SERP changes
- Pretend click behavior hasn’t shifted
- Wait until traffic drops to pay attention
The fundamentals haven’t changed. The visibility landscape has. Both things are true.
Where Google AI Overviews Appear (And How to Find Them at Scale)
Here are a few practical tips on how to find AI Overviews. This covers the fundamentals you need to know.
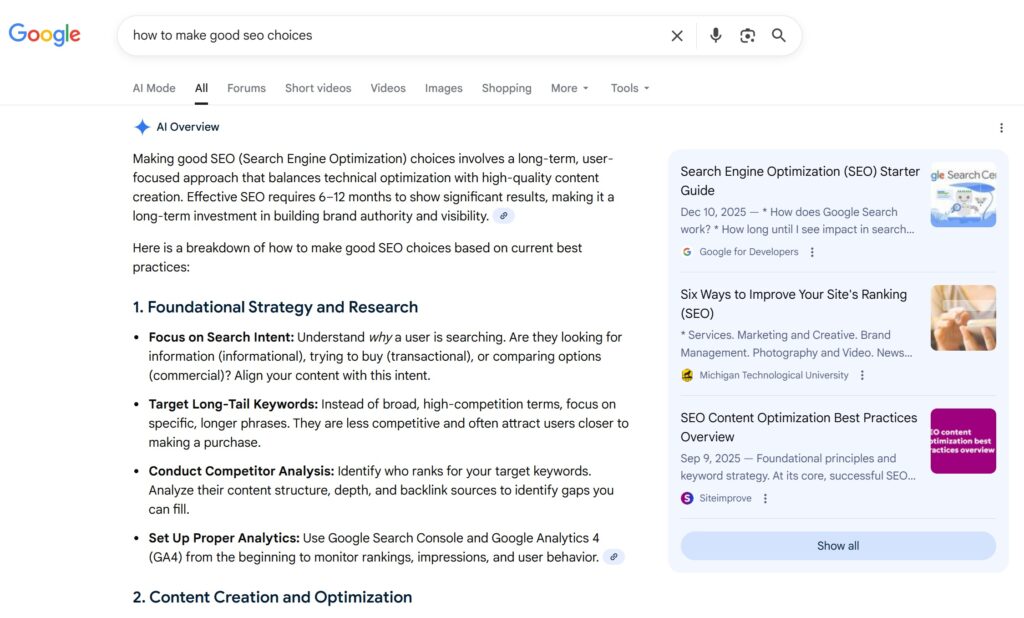
Which Search Queries Trigger AI Overviews
AI Overviews don’t appear on every search. They show up most consistently on certain query types:
Informational queries where users want explanations, definitions, or overviews. “What is,” “how does,” “why do” patterns trigger them frequently.
How-to and process queries where users want step-by-step guidance. Recipe searches, tutorial queries, troubleshooting questions.
Comparison queries where users are evaluating options. “X vs Y,” “best X for Y,” “difference between X and Y.”
Early-funnel research where users are exploring a topic before they have specific intent. These tend to be broader, more informational searches.
AI Overviews appear less often on:
Transactional queries with clear purchase intent. Google still wants to show product results here.
Navigational queries where users are looking for a specific site or page.
Local queries where map packs and business listings dominate.
Late-funnel queries where users are close to conversion and want specific options, not summaries.
Understanding this pattern helps you prioritize. If your traffic comes primarily from transactional or navigational queries, AI Overviews may not be your biggest concern. If you rely on informational content to drive top-of-funnel traffic, pay closer attention.
How to Identify Google AI Overviews in the Wild
The Manual Method
Open an incognito window. Search your target keywords. Note which ones trigger AI Overviews. This is slow but gives you ground truth.
A few things to watch for:
- Log out of your Google account
- Use incognito to avoid personalization
- Check from multiple locations if possible (VPN or proxy)
- Document what you see with screenshots
The manual method works for a handful of priority keywords. Once you understand what to look for, then you can confidently scale with tools.
The Tool-Assisted Method
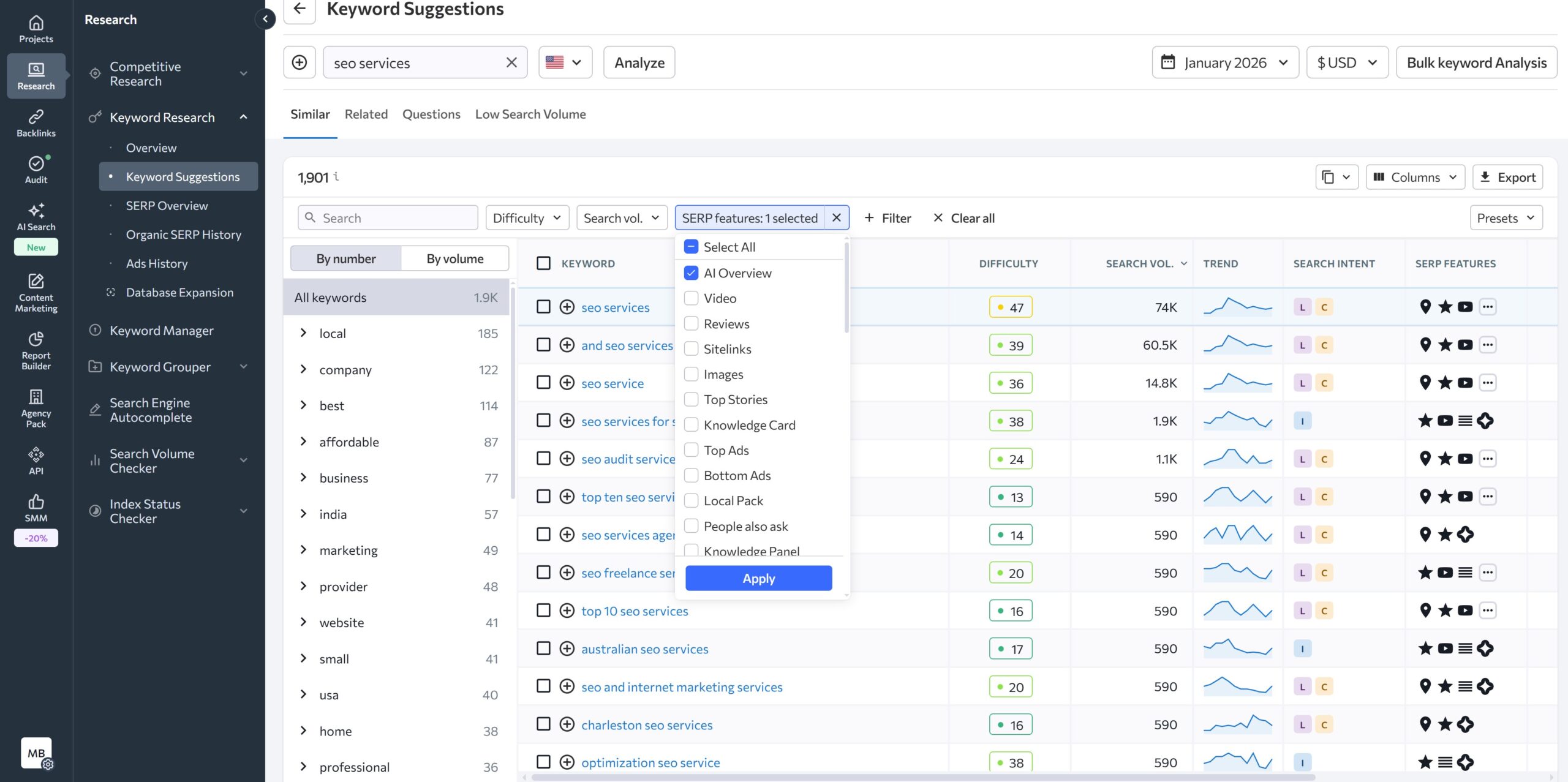
Most rank tracking tools now flag SERP features for their rank trackers and SERP analysis tools including AI Overviews. The workflow:
- Export your tracked keywords
- Filter by SERP feature: AI Overview present
- Cross-reference with your current rankings
- Identify where you rank but AI Overview appears above you
Tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, SEranking and others have added AI Overview detection. You don’t need a dedicated “AI SEO tool” for this. Your existing rank tracker probably already captures it. This shouldn’t be confused with tracking searches from LLM platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini or Claude. We’re talking about AI Overviews that show in traditional Google search results and disrupt the 10 blue links we’ve been going after.
Track which of your target keywords trigger AI Overviews and whether that percentage is growing or shrinking over time. This gives you a baseline. Without it, you’re guessing.
What Google AI Overviews Are Actually Built From
The Page-One Ranking Correlation
AI Overviews pull from pages that already rank on page one approximately 54% of the time. This isn’t speculation. Multiple analyses have shown strong overlap between the sources cited in AI Overviews and the top organic results for the same query. This varies from industry vertical to vertical, and continues to evolve every month.
What this confirms:
- Rankings still determine visibility
- Authority signals still matter
- The AI is synthesizing existing content, not finding hidden gems
If you rank positions 1-5 for a query and an AI Overview appears, there’s a high chance your content contributed to that summary. If you rank position 30, you’re not getting cited.
This is why “just do SEO” advice is directionally correct. The pages being pulled into AI Overviews earned that visibility through traditional ranking factors first.
Reverse Engineering What Google Rewards in AI Overviews

The SERP Deconstruction Process
For any target keyword, here’s the analysis workflow:
Step 1: Check if AI Overview appears
Search the keyword in incognito. Document whether an AI Overview shows up. If it doesn’t, you’re dealing with traditional SERP optimization only.
Step 2: List cited sources
Expand the AI Overview citations. Note and document every domain and URL that’s being cited. Note the order if there are multiple sources. You should also investigate semantically related searches to audit the aggregate of commonly cited sources. Such as identify that Reddit or Trust Pilot is a commonly cited source in your industry, as an example.
Step 3: Compare to organic results
Look at positions 1-10 in organic. How much overlap is there with the AI Overview citations? Are there any sources in the AI Overview that rank lower than expected in organic?
Step 4: Analyze the cited content
Visit the cited pages. Look for:
- Common subtopics all of them cover
- Angles or questions some cover that others don’t
- Content depth (word count, detail level)
- Format patterns (lists, tables, definitions)
- Authority signals (author credentials, citations, publication quality)
Step 5: Identify gaps
Compare your content to what’s being cited. Where are you falling short?
- Missing subtopics?
- Less depth on key areas?
- Poor structure or formatting?
- Weaker authority signals?
Step 6: Build your content brief
Use the gap analysis to plan updates. Be specific about what needs to be added, restructured, or improved. Don’t guess. Let the SERP analysis guide you.
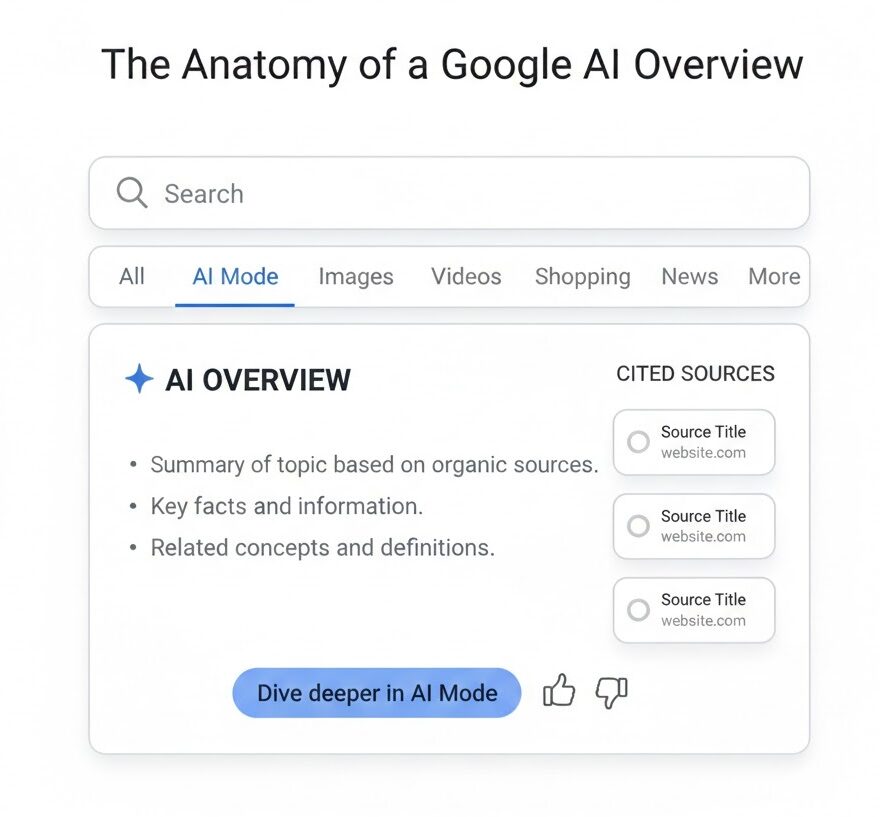
How to Structure Content for AI Overview Citations
The goal isn’t “optimizing for AI.” The goal is clarity, extractability, and completeness. Content that’s easy for a human to scan is also easy for an AI to summarize.
Content Information Architecture
Organize content with clear topical hierarchy. The main heading answers the primary query. Subheadings cover the natural follow-up questions someone would ask next.
Practical Structure
- H1: Primary topic/question
- H2s: Major subtopics or steps
- H3s: Supporting detail within each subtopic
- Short paragraphs that make one point each
Question-based subheadings work well for informational content because they match how people search. If someone asks “how long does X take,” having a subheading that addresses duration directly increases the chance that section gets pulled.
Content Formatting and Signals That Get Cited
Certain formats are more extractable than others:
Definition blocks. When you define a term, make it clean. “X is [clear definition].” Put it near the top of relevant sections. AI Overviews frequently pull these.
Step-by-step sections. Numbered lists for processes. Each step should be self-contained enough to make sense in isolation.
Comparison tables. When comparing options, tables are more scannable than paragraphs. They also give AI systems structured data to work with.
Concise summaries. After detailed sections, a brief summary paragraph reinforces the key point. This gives the AI multiple places to pull from.
Entity-rich explanations. Mention specific names, places, products, or concepts that are relevant to the topic. Entities help establish what your content is about.
Topical authority over keyword density. Cover the subject comprehensively. Pages that address the full scope of a topic get cited more than pages that target one keyword narrowly.
Trust signals. Author bios, credentials, publication dates, citations to primary sources. These build trust with both users and Google’s systems.
Recency where relevant. For topics where freshness matters, outdated content gets passed over. Check that statistics, examples, and recommendations reflect current reality.
The caveat here is that injecting these elements into existing content can be a major benefit in appearing in AI Overviews and LLM searches. But you don’t want to completely rewrite all your content and water it down. Shortening and simplifying everything will mean your content lacks nuance and unique value that AI Overviews and LLMs love to cite. Don’t fall into a pitfall of generic content that doesn’t differentiate itself from what is already in their index.
Measuring AI Overview Impact on Your Traffic
What You Can and Can’t Track with AI Overviews
There’s no direct “AI Overview rank” metric yet. Google doesn’t tell you when your content gets pulled into an AI Overview or how prominently. Third-party tools are making progress on detection, but granular attribution remains limited.
What you can track:
SERP feature presence. Which keywords trigger AI Overviews? Is that percentage increasing or decreasing for your keyword portfolio?
Click-through rate shifts. If AI Overviews are cannibalizing clicks, you’ll see CTR decline even when rankings stay stable. Compare CTR trends for keywords with AI Overviews vs. those without.
Impression changes. Sometimes AI Overviews push organic results lower on the page. Impressions may hold steady while clicks decline if users are getting answers from the AI Overview without scrolling.
Branded vs. non-branded performance. AI Overviews impact non-branded informational queries more than branded searches. Segment your data to see where changes are happening.
A Practical AI Overview Monitoring Framework
Segment Your Keywords
Create two groups in your rank tracking tool:
- Keywords where AI Overviews appear
- Keywords where AI Overviews don’t appear
Track each group separately. If you see traffic decline in the AI Overview group while the other holds steady, you have a signal.
Monitor These Metrics Monthly
- Average CTR by segment
- Traffic trends by segment
- Ranking stability (how much are positions fluctuating?)
- Featured snippet volatility (these often overlap with AI Overview presence)
Diagnosing Traffic Drops
When traffic declines, rule out other causes before blaming AI Overviews:
- Did rankings actually drop? Check position changes.
- Did a core update hit your site? Check timing against algorithm rollouts.
- Is the content outdated or lower quality than competitors?
- Are seasonal traffic patterns explaining the change?
AI Overviews may be the cause. They may not be. Measure before you assume.
Why “Just Do SEO” Is Right and Also Incomplete
Traditional SEO remains the foundation. The pages that rank well in organic search are the same pages that get cited in AI Overviews. If you’re doing solid SEO work, you’re already positioned.
But stopping there misses important shifts:
Visibility has changed. AI Overviews occupy prime real estate above organic results. Even if your content contributes to the summary, users may not click through to your site.
Click behavior has changed. For some queries, users get their answer from the AI Overview and leave. Zero-click searches have been increasing for years. AI Overviews accelerate that trend.
SERP real estate is competitive. If an AI Overview, featured snippet, People Also Ask, and ads all appear before organic results, position 1 isn’t what it used to be.
The practical response:
- Keep doing fundamental SEO work
- Add SERP feature analysis to your process
- Track where AI Overviews appear in your keyword portfolio
- Structure content to maximize citation potential
- Measure impact so you know what’s actually happening
This isn’t panic. It’s paying attention.
The No-Hype AI Overview Playbook
A repeatable system for dealing with AI Overviews:
Audit your keyword portfolio for AI Overview presence. Export your tracked keywords. Flag which ones trigger AI Overviews. Calculate what percentage of your traffic-driving keywords are affected.
Prioritize based on impact. Not all AI Overviews matter equally. Focus on keywords that drive significant traffic or conversions, show declining CTR despite stable rankings, or represent important topics for your business.
Analyze cited sources for priority keywords. Run the SERP deconstruction process. Document what’s being cited and identify gaps in your content.
Update content based on gap analysis. Improve structure, add missing subtopics, strengthen formatting, update outdated information. Make changes based on evidence, not guesses.
Track results by segment. Monitor the AI Overview keyword segment separately. Watch for CTR recovery, traffic stabilization, or citation appearances in rank tracking tools that support this.
Repeat quarterly. AI Overviews are still rolling out and evolving. What triggers them today may change. Build this analysis into your regular SEO review process.
Don’t optimize for AI alone. Optimize so well that AI systems have no choice but to use you as a source. That’s always been the job. The stakes are just more visible now.


